In this blog post, we’ll delve into the process of creating a Pulumi Resource provider sourced from a Terraform Provider developed with the Terraform Plugin Framework. Our focus will be on leveraging the bridge package to facilitate this transition seamlessly. To illustrate, we’ll demonstrate bridging the InfluxDB Terraform provider to Pulumi.

Table of Contents
Prerequisites
Before delving further, it’s essential to possess a foundational understanding of Terraform providers, Pulumi resource providers, and InfluxDB.
Ensure the following tools are installed and present in your %PATH:
• pulumictl
• Go 1.17 or latest
• NodeJS 14.x
• Yarn
• TypeScript
• Python
• .NET
Why Bridge a Terraform Provider to Pulumi
The mature and vibrant Terraform Providers ecosystem benefits from contributions by numerous industry leaders in cloud and infrastructure. By bridging Terraform Providers to Pulumi, organizations gain access to reliable and battle-tested infrastructure management capabilities.
How the bridge works
The bridge operates across two significant phases: design-time and runtime.
During design-time, the bridge meticulously examines the schema of a Terraform Provider. However, it’s important to note that this process is applicable solely to providers constructed with static schemas.
Moving on to the runtime phase, the bridge establishes a connection between the Pulumi engine and the designated Terraform Provider by harnessing Pulumi’s RPC interfaces. This interaction heavily relies on the Terraform provider schema, facilitating tasks such as validation and the computation of differences.
How to bridge a provider
Pulumi provides two options for initializing your project: you can either utilize the template repository offered by Pulumi, or opt for the community-supported cookiecutter template.
If you choose the cookiecutter template, setting up an initial version is straightforward — just specify a few configuration settings. However, if you prefer the template repository route, follow the steps outlined below to get started:
- To begin, navigate to the template repository and select Use this template.
- Then, ensure the following options are configured:
- Owner: Your GitHub organization or username.
- Repository name: Preface your repository name with pulumi as per standard practice. For instance, pulumi-influxdb.
- Description: Provide a brief description of your provider.
- Repository type: Set it to Public.
- After configuring these options, proceed to clone the generated repository.
- Execute the following command to update the files, replacing placeholders with the name of your provider.
make prepare NAME=influxdb REPOSITORY=github.com/komminarlabs/pulumi-influxdb
- This will do the following:
- Rename folders in provider/cmd to pulumi-resource-influxdb and pulumi-tfgen-influxdb.
- Replace dependencies in provider/go.mod to reflect your repository name.
- Find and replace all instances of the boilerplate xyz with the NAME of your provider.
- Ensure to accurately set your GitHub organization or username in all files where your provider is referenced as a dependency.
examples/go.modprovider/resources.gosdk/go.modprovider/cmd/pulumi-resource-influxdb/main.goprovider/cmd/pulumi-tfgen-influxdb/main.go
Create a Shim
Although the New() provider function resides within an internal package, referencing it in an external Go project isn’t straightforward. However, it’s still achievable through Go linker techniques.
- Create a provider/shim directory.
mkdir provider/shim
- Add a
go.modfile with the following content.
module github.com/komminarlabs/terraform-provider-influxdb/shim
go 1.22
require (
github.com/hashicorp/terraform-plugin-framework v1.6.0
github.com/komminarlabs/terraform-provider-influxdb v1.0.1
)
- Add a
shim.gofile with the following content.
package shim
import (
tfpf "github.com/hashicorp/terraform-plugin-framework/provider"
"github.com/komminarlabs/terraform-provider-influxdb/internal/provider"
)
func NewProvider() tfpf.Provider {
return provider.New("dev")()
}
Import the New Shim Provider
In provider/resources.go import the shim package.
package influxdb
import (
"fmt"
"path"
// Allow embedding bridge-metadata.json in the provider.
_ "embed"
influxdbshim "github.com/komminarlabs/terraform-provider-influxdb/shim"
pf "github.com/pulumi/pulumi-terraform-bridge/pf/tfbridge"
"github.com/pulumi/pulumi-terraform-bridge/v3/pkg/tfbridge"
"github.com/pulumi/pulumi-terraform-bridge/v3/pkg/tfbridge/tokens"
shim "github.com/pulumi/pulumi-terraform-bridge/v3/pkg/tfshim"
"github.com/pulumi/pulumi/sdk/v3/go/common/resource"
// Import custom shim
"github.com/komminarlabs/pulumi-influxdb/provider/pkg/version"
)
Instantiate the Shim Provider
- In
provider/resources.go, replaceshimv2.NewProvider(influxdb.Provider())withpf.ShimProvider(influxdbshim.NewProvider())
func Provider() tfbridge.ProviderInfo {
prov := tfbridge.ProviderInfo{
// Instantiate the Terraform provider
P: pf.ShimProvider(influxdbshim.NewProvider()),
}
- Edit
provider/go.modand addgithub.com/komminarlabs/terraform-provider-influxdb/shim v0.0.0to the requirements.
module github.com/komminarlabs/pulumi-influxdb/provider
go 1.22
replace (
github.com/hashicorp/terraform-plugin-sdk/v2 => github.com/pulumi/terraform-plugin-sdk/v2 v2.0.0-20240202163305-e2a20ae13ef9
github.com/komminarlabs/terraform-provider-influxdb/shim => ./shim
)
require (
github.com/komminarlabs/terraform-provider-influxdb/shim v0.0.0
github.com/pulumi/pulumi-terraform-bridge/pf v0.29.0
github.com/pulumi/pulumi-terraform-bridge/v3 v3.76.0
github.com/pulumi/pulumi/sdk/v3 v3.108.1
)
Build the Provider
Build Generator
Create the schema by running the following command.
make tfgen
Add Mappings
In this section we will add the mappings that allow the interoperation between the Pulumi provider and the Terraform provider. Terraform resources map to an identically named concept in Pulumi. Terraform data sources map to plain old functions in your supported programming language of choice.
Resource mapping
For every resource present in the provider, include an entry in the Resources property of the tfbridge.ProviderInfo structure.
Resources: map[string]*tfbridge.ResourceInfo{
"influxdb_authorization": {Tok: tfbridge.MakeResource(mainPkg, mainMod, "Authorization")},
"influxdb_bucket": {Tok: tfbridge.MakeResource(mainPkg, mainMod, "Bucket")},
"influxdb_organization": {Tok: tfbridge.MakeResource(mainPkg, mainMod, "Organization")},
},
Data Source mapping
Add an entry in the DataSources property of the tfbridge.ProviderInfo for each data source included in the provider.
DataSources: map[string]*tfbridge.DataSourceInfo{
"influxdb_authorization": {Tok: tfbridge.MakeDataSource(mainPkg, mainMod, "getAuthorization")},
"influxdb_authorizations": {Tok: tfbridge.MakeDataSource(mainPkg, mainMod, "getAuthorizations")},
"influxdb_bucket": {Tok: tfbridge.MakeDataSource(mainPkg, mainMod, "getBucket")},
"influxdb_buckets": {Tok: tfbridge.MakeDataSource(mainPkg, mainMod, "getBuckets")},
"influxdb_organization": {Tok: tfbridge.MakeDataSource(mainPkg, mainMod, "getOrganization")},
"influxdb_organizations": {Tok: tfbridge.MakeDataSource(mainPkg, mainMod, "getOrganizations")},
},
Build Provider
Generate the provider binary by executing the following command:
make provider
Build SDKs
Compile the SDKs across the range of languages supported by Pulumi, and validate that the provider code adheres to the Go language standards.
make build_sdks
make lint_provider
Write documentation
Incorporate a docs/ directory containing template pages that correspond to the different tabs typically found on a package page within the Pulumi Registry.
Overview, installation, and configuration
_index.md, which will be displayed on the Overview tab for your package in the Pulumi Registry. The title of this page should align with the package display name, serving as the heading shown on the package detail page. The Overview section is an ideal space to include a concise description of your package’s functionality along with a straightforward example.
---
title: InfluxDB
meta_desc: Provides an overview of the InfluxDB Provider for Pulumi.
layout: package
---
installation-configuration.md, this file will be displayed on your package’s Installation & Configuration tab in the Pulumi Registry. Utilize this page to provide comprehensive instructions on setting up your package, covering aspects such as authentication procedures. Additionally, include a list of configuration options available for use with your package.
---
title: InfluxDB Installation & Configuration
meta_desc: Information on how to install the InfluxDB provider.
layout: package
---
Publish your package
After authoring and thoroughly testing your package locally, the next step is to publish it to make it accessible to the Pulumi community. This process involves publishing several artifacts:
- The npm, NuGet, Java, and Python SDK packages to the npm Registry, the NuGet Gallery, Maven Central and the Python Package Index
- The Go module to your Git repository, by adding a tag.
- The binary Pulumi resource provider plugin to a binary hosting provider of your choice.
To streamline this process, we’ll leverage GitHub Actions. Below are the GitHub Actions you’ll use for this purpose.
name: release
on:
push:
tags:
- v*.*.*
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
NODE_AUTH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.NPM_TOKEN }}
NPM_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.NPM_TOKEN }}
PUBLISH_NPM: true
NPM_REGISTRY_URL: https://registry.npmjs.org
NUGET_PUBLISH_KEY: ${{ secrets.NUGET_PUBLISH_KEY }}
NUGET_FEED_URL: https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json
PUBLISH_NUGET: true
PYPI_PASSWORD: ${{ secrets.PYPI_API_TOKEN }}
PYPI_USERNAME: "__token__"
PYPI_REPOSITORY_URL: ""
PUBLISH_PYPI: true
jobs:
publish_binary:
name: Publish Binary
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
contents: write
strategy:
fail-fast: true
matrix:
goversion:
- 1.22.x
steps:
- name: Checkout Repo
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Unshallow clone for tags
run: git fetch --prune --unshallow --tags
- name: Install Go
uses: actions/setup-go@v3
with:
go-version: ${{matrix.goversion}}
- name: Install pulumictl
uses: jaxxstorm/action-install-gh-release@v1.10.0
with:
repo: pulumi/pulumictl
- name: Set PreRelease Version
run: echo "GORELEASER_CURRENT_TAG=v$(pulumictl get version --language generic)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Run GoReleaser
uses: goreleaser/goreleaser-action@v2
with:
args: -p 3 release --rm-dist
version: latest
publish_sdk:
name: Publish SDK
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
needs: publish_binary
strategy:
fail-fast: true
matrix:
dotnetversion:
- 6.0.x
goversion:
- 1.22.x
nodeversion:
- 16.x
pythonversion:
- "3.9"
language:
- nodejs
- python
- dotnet
- go
steps:
- name: Checkout Repo
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Unshallow clone for tags
run: git fetch --prune --unshallow --tags
- name: Install Go
uses: actions/setup-go@v5
with:
go-version: ${{ matrix.goversion }}
- name: Install pulumictl
uses: jaxxstorm/action-install-gh-release@v1.11.0
with:
repo: pulumi/pulumictl
- name: Install pulumi
uses: pulumi/actions@v4
- if: ${{ matrix.language == 'nodejs'}}
name: Setup Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v1
with:
node-version: ${{matrix.nodeversion}}
registry-url: ${{env.NPM_REGISTRY_URL}}
- if: ${{ matrix.language == 'dotnet'}}
name: Setup DotNet
uses: actions/setup-dotnet@v1
with:
dotnet-version: ${{matrix.dotnetversion}}
- if: ${{ matrix.language == 'python'}}
name: Setup Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v1
with:
python-version: ${{matrix.pythonversion}}
- name: Build SDK
run: make build_${{ matrix.language }}
- if: ${{ matrix.language == 'python' && env.PUBLISH_PYPI == 'true' }}
name: Publish package to PyPI
uses: pypa/gh-action-pypi-publish@release/v1
with:
user: ${{ env.PYPI_USERNAME }}
password: ${{ env.PYPI_PASSWORD }}
packages_dir: ${{github.workspace}}/sdk/python/bin/dist
- if: ${{ matrix.language == 'nodejs' && env.PUBLISH_NPM == 'true' }}
uses: JS-DevTools/npm-publish@v1
with:
access: "public"
token: ${{ env.NPM_TOKEN }}
package: ${{github.workspace}}/sdk/nodejs/bin/package.json
- if: ${{ matrix.language == 'dotnet' && env.PUBLISH_NUGET == 'true' }}
name: publish nuget package
run: |
dotnet nuget push ${{github.workspace}}/sdk/dotnet/bin/Debug/*.nupkg -s ${{ env.NUGET_FEED_URL }} -k ${{ env.NUGET_PUBLISH_KEY }}
echo "done publishing packages"
Publish the documentation
To publish your package on the Pulumi Registry, all package documentation is managed through the pulumi/registry repository on GitHub. Here’s how to proceed:
- Fork and clone the
pulumi/registryrepository to your local machine. - Add your package to the community package list within the repository.
{
"repoSlug": "komminarlabs/pulumi-influxdb",
"schemaFile": "provider/cmd/pulumi-resource-influxdb/schema.json"
},
- After making the necessary changes to add your package to the community package list, open a pull request with the modifications. Subsequently, await review from a member of the Pulumi team.
- Upon review, a Pulumi employee will collaborate with you to finalize the steps required for publishing your Pulumi Package.
Using the provider
Now that we have successfully built and published our Pulumi provider, let’s proceed to utilize it for resource creation. In this instance, we’ll opt for Python as our preferred programming language.
Installation
mkdir python-influxdb
cd python-influxdb
# (Go through the prompts with the default values)
pulumi new python
# Use the virtual Python env that Pulumi sets up for you
source venv/bin/activate
# Install the provider package
pip install komminarlabs_influxdb
Set up environment
You have the option to configure the provider either through environment variables or by utilizing the Pulumi.dev.yaml file.
export INFLUXDB_URL="http://localhost:8086"
export INFLUXDB_TOKEN="***"
pulumi config set influxdb:url http://localhost:8086
pulumi config set influxdb:token *** --secret
Add the following contents to the __main__.py file
"""A Python Pulumi program"""
import pulumi
import komminarlabs_influxdb as influxdb
organization = influxdb.Organization(
"IoT",
name="IoT",
description="IoT organization"
)
bucket = influxdb.Bucket(
"signals",
org_id=organization.id,
name="signals",
description="This is a bucket to store signals",
retention_period=604800,
)
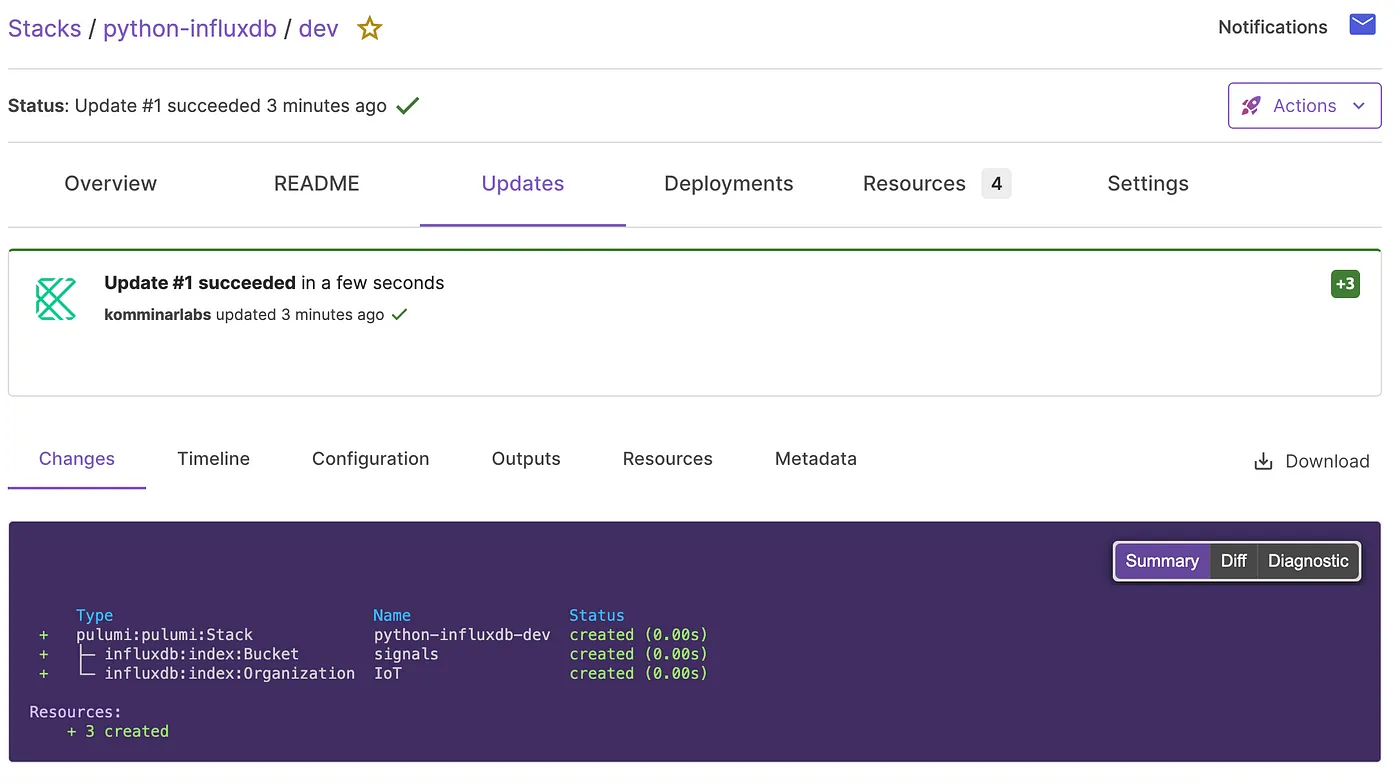
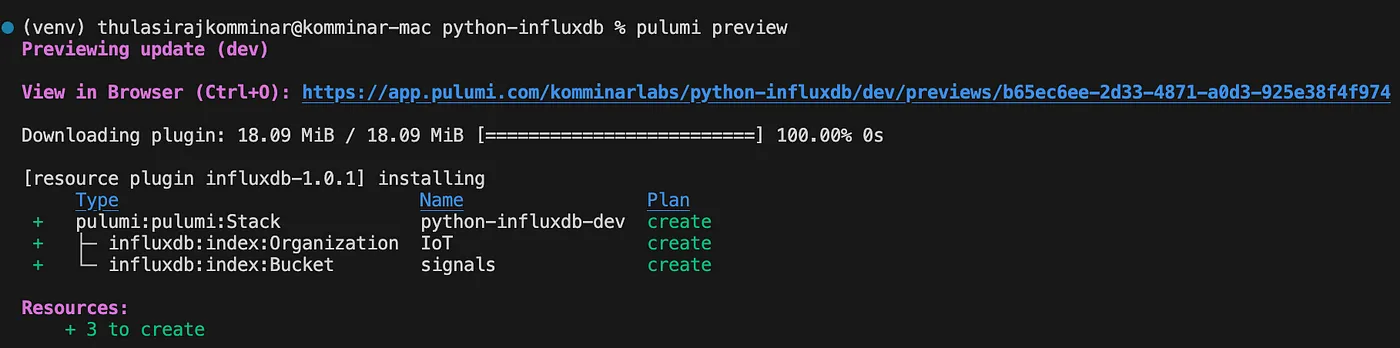
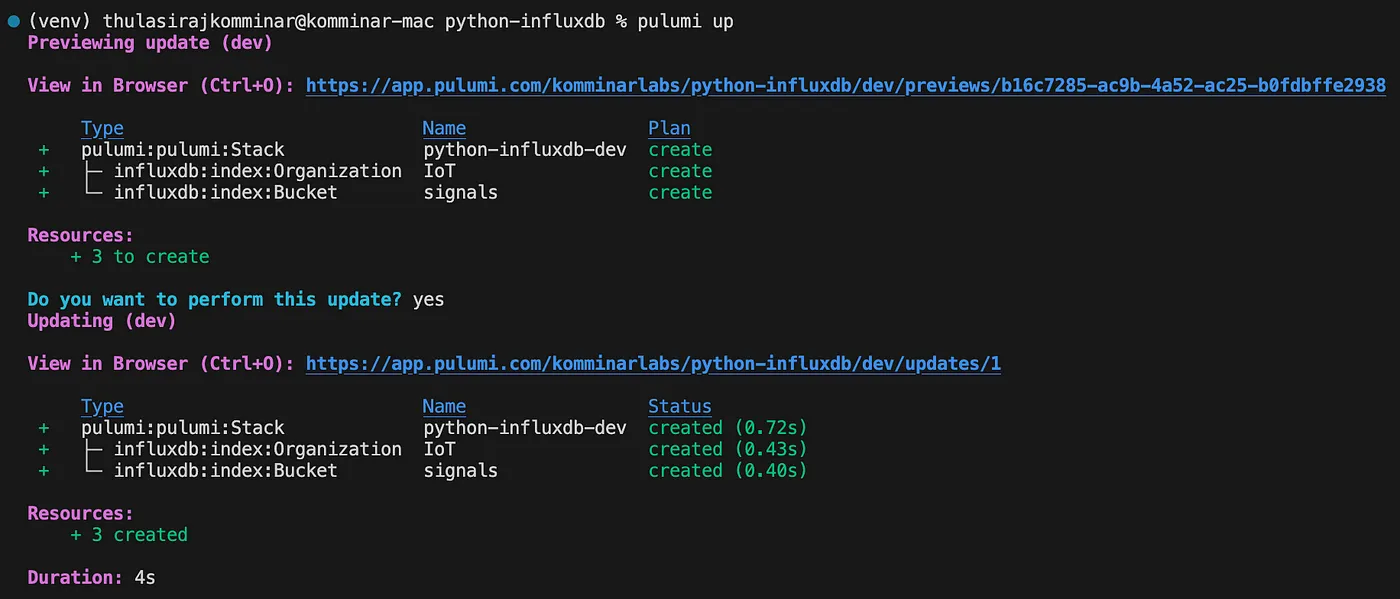
Next, execute the pulumi preview command to view a preview of the updates to an existing stack. Follow this by running pulumi up to either create or update the resources within the stack.
You can also view the stacks in Pulumi cloud.